Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear French mathematician JosephOn Earth, the major greenhouse gases are water vapor, which causes about 36–70 percent of the greenhouse effect (not including clouds);Carbon dioxide (CO 2), which causes 9–26 percent;
Greenhouse Effect Its Causes And Effect List Of Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse effect greenhouse gases images
Greenhouse effect greenhouse gases images- ,853 greenhouse effect stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See greenhouse effect stock video clips of 9 greenhouse effect diagram commercial spraying water on plants greenhouse gas effect global warming posters sun earth diagram energy poster global warming global warming solutions sun radiating to a plant 3,528 greenhouse gases stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See greenhouse gases stock video clips of 36 sun radiating to a plant thermal radiation effects global warming greenhousegases gases in atmosphere light pollution effect gases cartoon atmosphere gases atmospheric gases cartoon global warming Try these




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activitiesIn 19, CO 2 accounted for about 80 percent of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals)
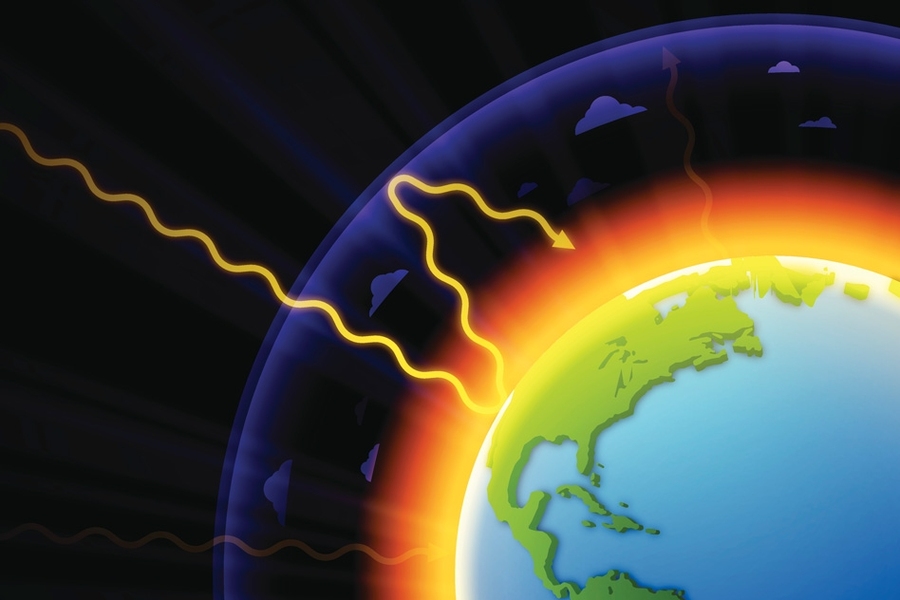
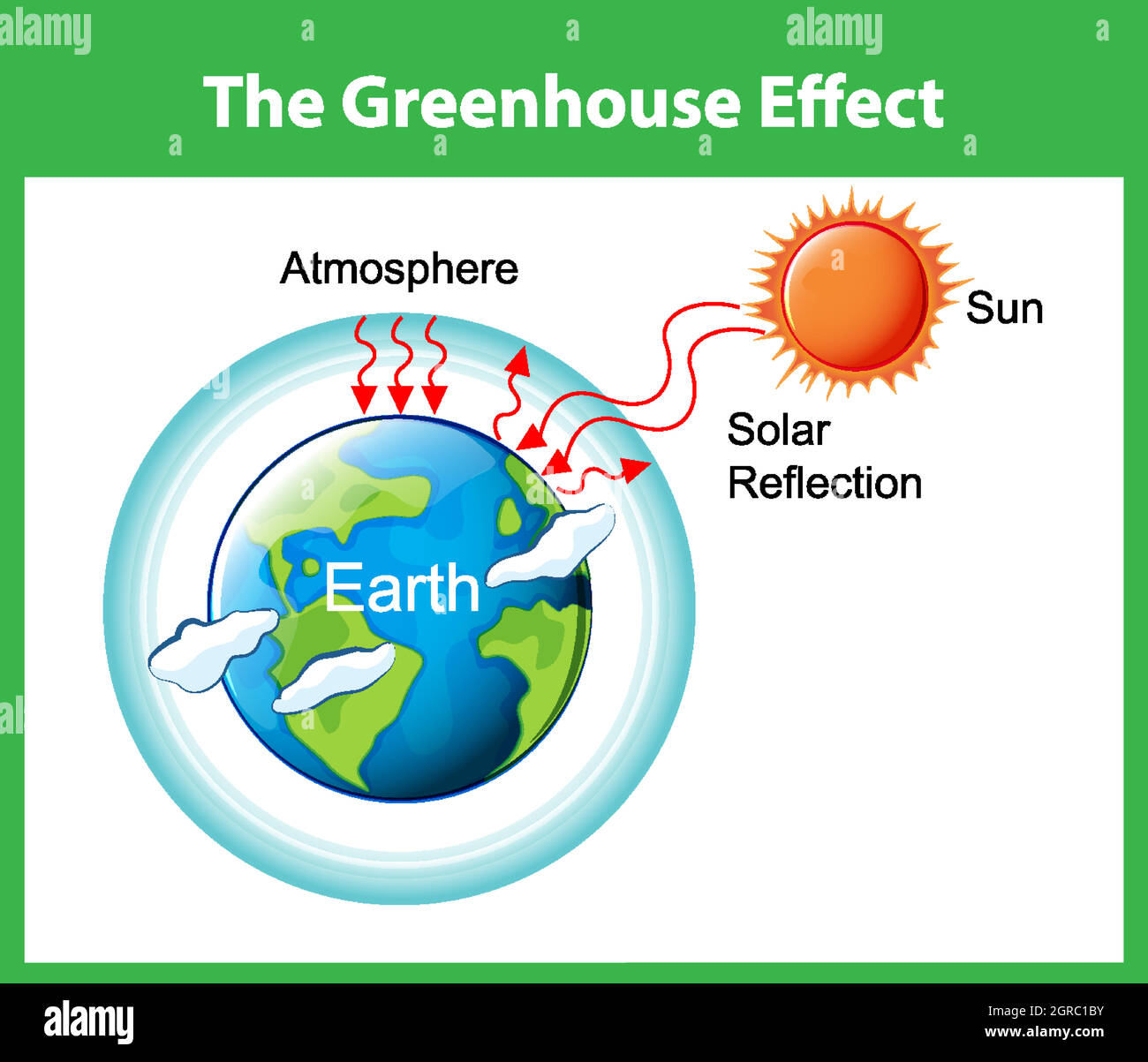
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming itThe greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxidesAnd ozone, which causes 3–7 percentThe issue is how the strength of the greenhouse effect changes when human
Some of the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are caused by humans Whenever we burn anything, such as— gasoline in our cars and trucks, jet fuel in our planes, coal in our factories or powerplants, trees to clear the land for farming —we pollute our atmosphere with carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide Although carbon monoxide does not The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Greenhouse effect is the mechanism by which thermal radiation from earth's surface is reabsorbed by greenhouse gases and redirected in all directions Some of the major green house gases are




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science
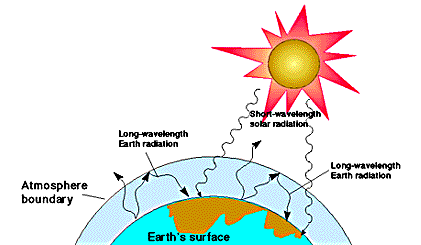
Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect Perhaps the most impressive of cloud formations, cumulonimbus (from the Latin for "pile" and "rain cloud") clouds form due to vigorous convection (rising and overturning) of warm, moist and unstable air The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effectUnderstanding Low Everywhere How will humans react Surprise changes WA Increased winter flooding Increased landslides Overall forest health Coastal erosion The greenhouse effect certain "greenhouse" gases in the atmosphere permit sunlight to pass through the atmosphere, but absorb much of the infrared (heat) radiation from Earth's surface



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions



Greenhouse Effect Graphic High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
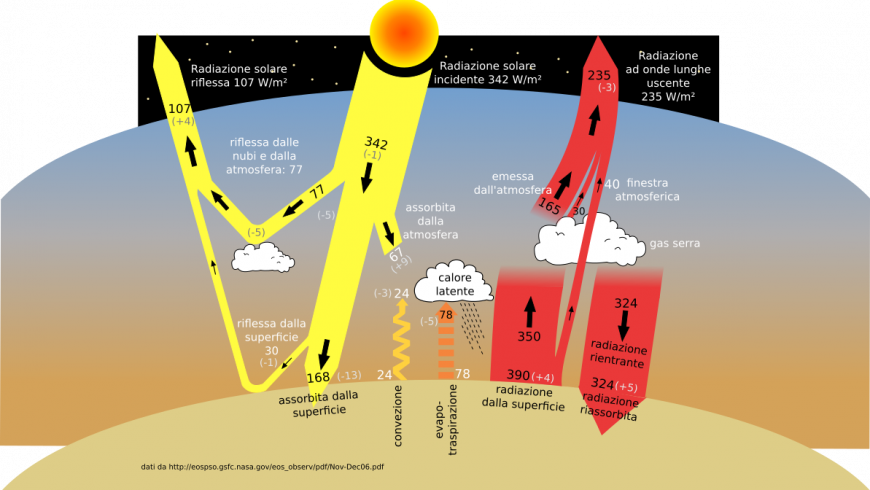
Radiative forcing of each gas, ie the capacity to trap the energy going from our Planet into Space;Browse 343,699 greenhouse effect stock photos and images available, or search for greenhouse effect diagram or greenhouse effect illustration to find more great stock photos and pictures Man on a rooftop looks at approaching flames as the Springs fire continues to grow on near Camarillo, CaliforniaA greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3)Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would




Greenhouse Effect Its Causes And Effect List Of Greenhouse Gases



1
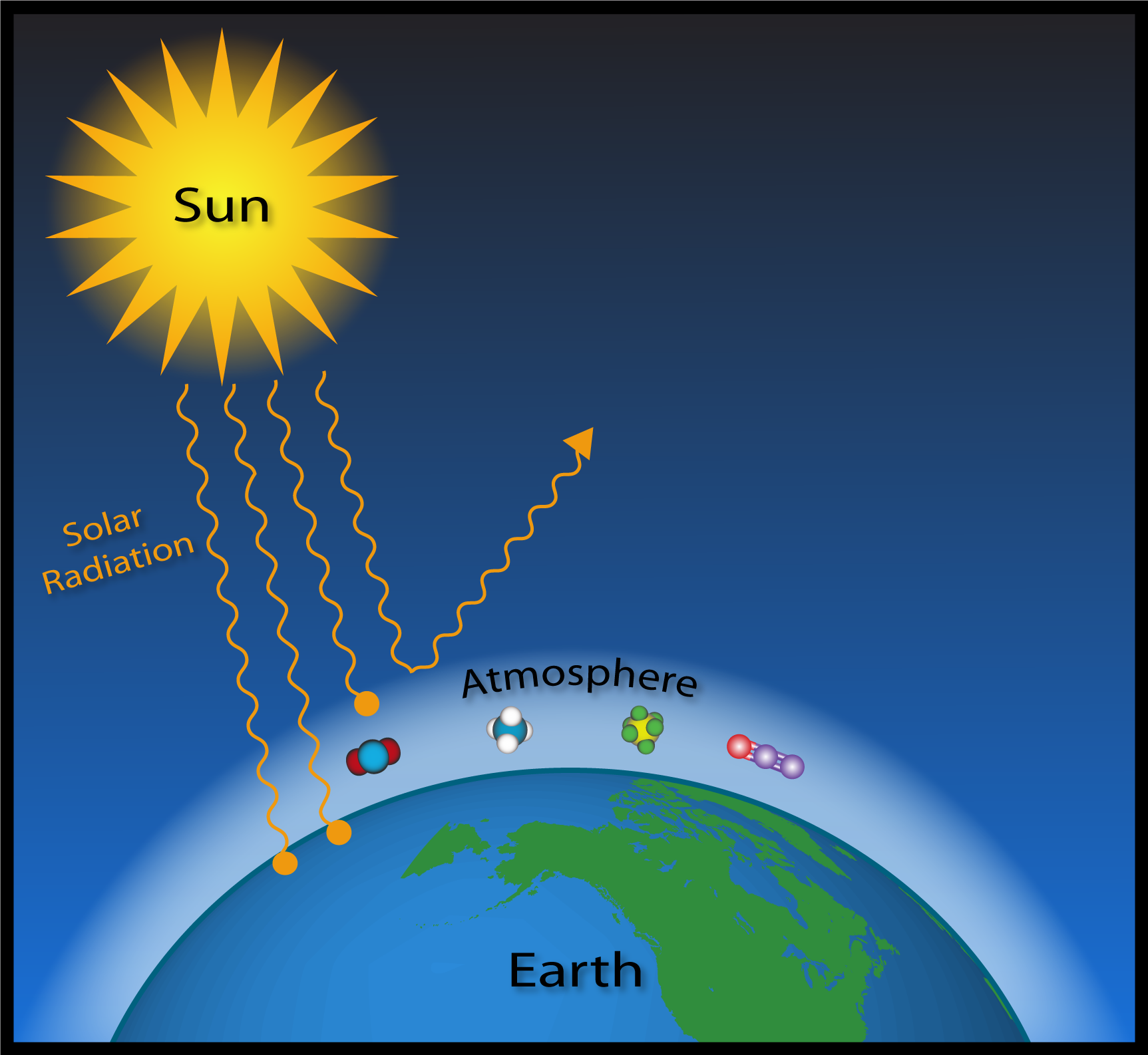
Amplifying the greenhouse effect Like other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent to incoming sunlight But unlike those gases, greenhouse gases are not transparent to outgoing heat (longwave infrared radiation), which radiates from the sunwarmed surface of Earth day and night Carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases such as methane cause heat to become trapped in Earth's atmosphere, leading to a warming effect Levels of carbon dioxide in our atmosphere are more than 50% higher than before the Industrial Revolution, according to statistics from the Met OfficeMethane (CH 4), which causes 4–9 percent;



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
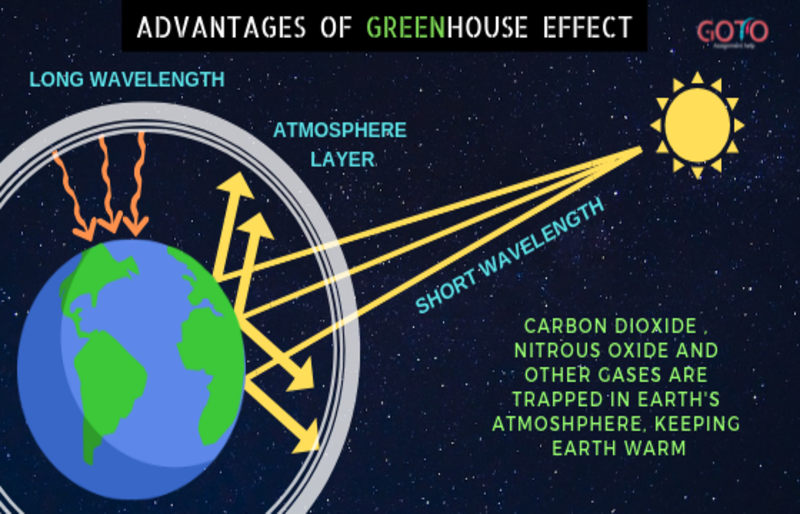



The Advantages Of Greenhouse Effect And The Role Of Greenhouse Gases
The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight Cool greenhouse gases high in Earth's atmosphere typically trap heat by absorbing infrared radiation emitted by our planet's warm surface before it reaches space Thanks to its release by many human activities, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is one of the most notorious of these planetwarming gases, but water vapor is a strong greenhouse gas, tooGreenhouse gases trap the incoming solar radiation, these gases include Carbon Dioxide, CFCs, Methane, Nitrous Oxides and other Halocarbons These are released by human activity We need the Greenhouse effect to maintain life on earth as we know ithowever if we keep adding to the Greenhouse gases there will be many changes
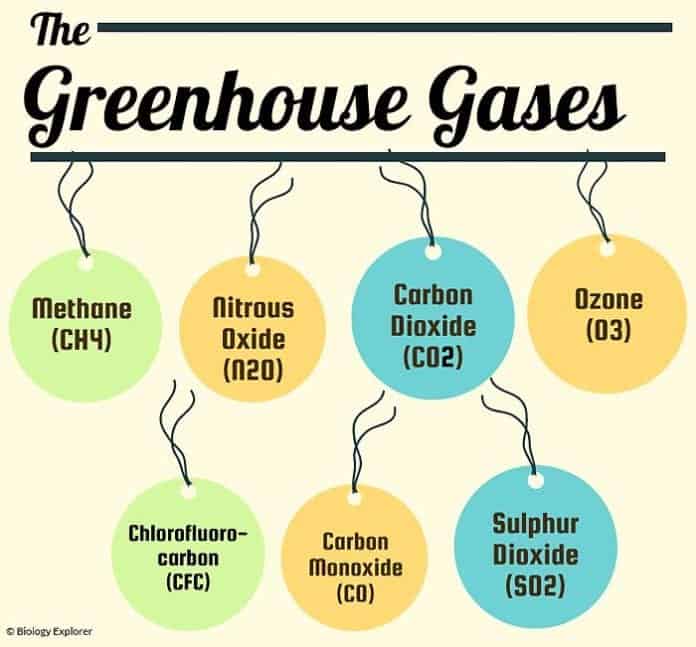



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
The greenhouse effect has kept the Earth's average temperature a good deal higher for billions of years, making it possible for life as we know it to evolve Over the past several millennia the average Earth temperature has been about 15 °C (59 °F) The figure below illustrates how greenhouse gases keep the Earth warmer than it would be Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape That's exactly how greenhouse gases act324 Greenhouse Gas Effect Premium High Res Photos Browse 324 greenhouse gas effect stock photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images electricity pylons and two coal fired power plants with pollution greenhouse gas effect stock pictures, royaltyfree photos & images



Greenhouse Effect Body Used Water Process Earth Plants Form Energy Gas




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
Carbon dioxide is the gas most responsible for the greenhouse effect because it is the most abundant and it persists in the atmosphere for 3001,000 years VectorMine /Persistence in the atmosphere of The major contributor to greenhouse gases was the ruminating process During a cow's digestion process, as food enters the stomach, it mixes with bacteria, which breaks the food down and produces methane (a greenhouse gas) Roughly minutes later, the food returns to the cow's mouth as cud, which it chews, thereby releasing methane into the air
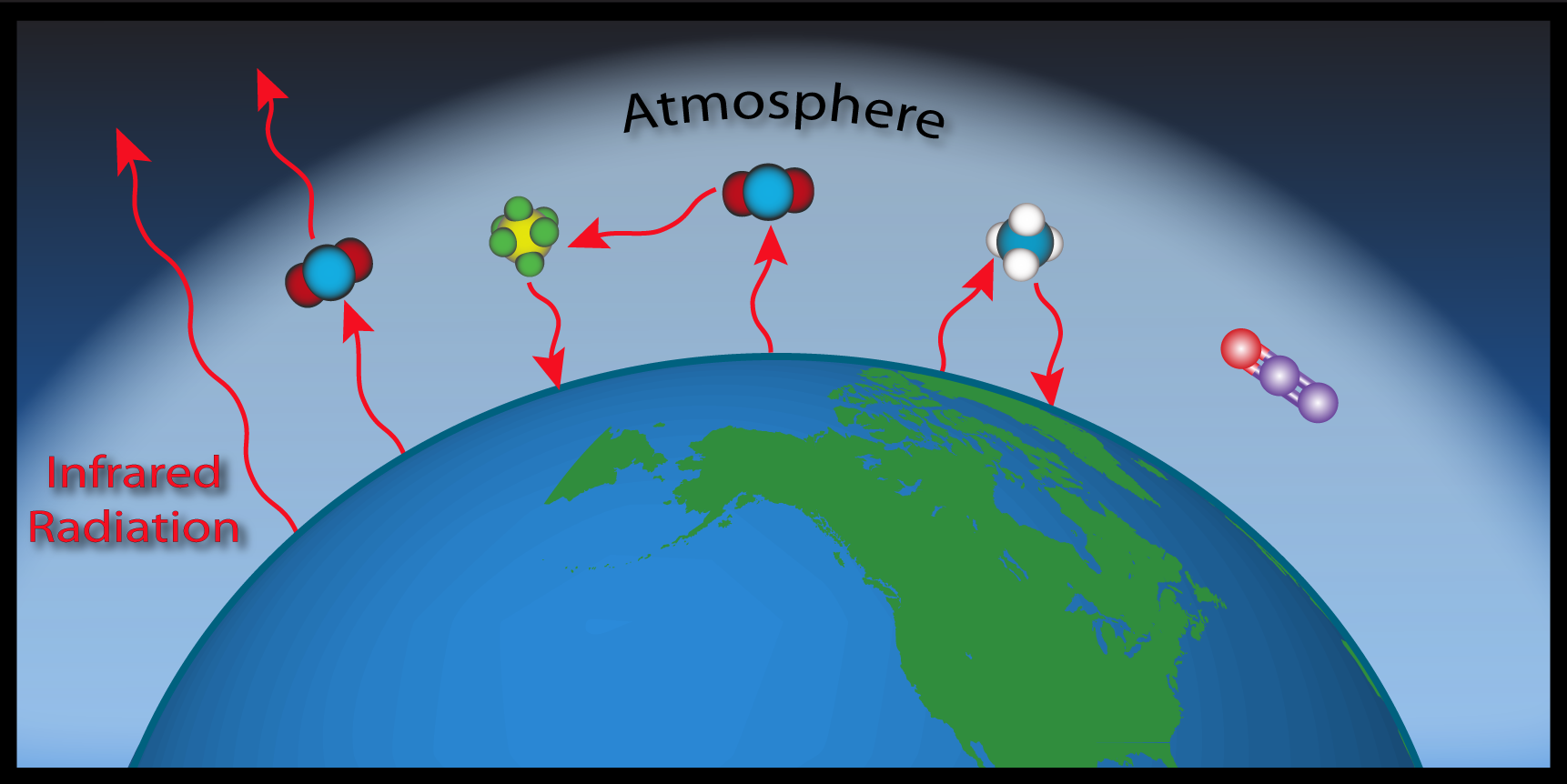



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
WHAT IS THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action — through activities such as industry, What Are Greenhouse Gases? The greenhouse effect is the process thanks to which Earth has a higher temperature than it would have without it The gases that radiate heat also known as greenhouse gases absorb the energy radiated out by the Earth and reflect a part of it back to Earth
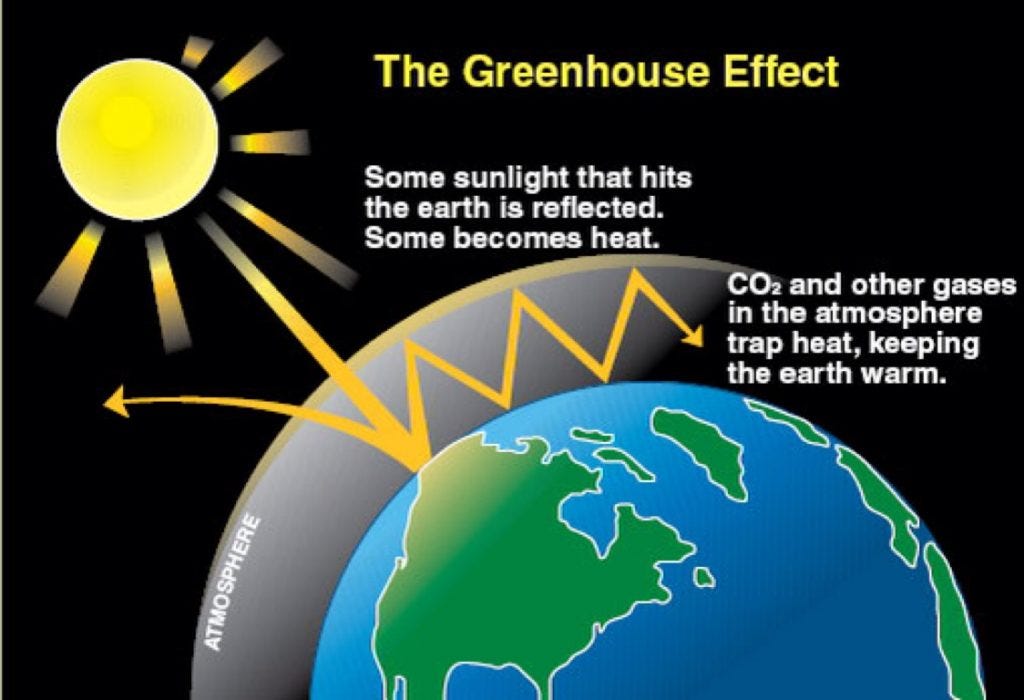



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
The greenhouse effect occurs when the sun's rays reach the Earth's atmosphere and the majority of the radiation bounces back out into space When this happens, a small portion is absorbed by chemicals in our atmosphere These are known as greenhouse gases By looking at air bubbles from hundreds of thousands of years ago until todayAtmosphere & Greenhouse Gases The natural greenhouse effect is necessary for the temperature of earth to support current life systems The enhanced greenhouse effect caused by a greater buildup of carbon dioxide and methane (and other greenhouse gases) leads to less radiated heat leaving the atmosphere, resulting in warmer global temperatures This is called the greenhouse effect, and the molecules that trap the heat are called greenhouse gases Even though greenhouse gases don't make a hard surface like the glass of a greenhouse, but because they have a similar effect in keeping our planet warm, the term "Greenhouse Effect" is a good description




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Textbook Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Layer Download Scientific Diagram
The goal is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from landfills Rich Pedroncelli A pizza box is mixedin with other compostable items awaiting composting at the Anaerobic Composter Facility in Comparing greenhouse gases In order to calculate the contribution of the different gases to the greenhouse effect, three fundamental parameters must be taken into consideration concentration in the atmosphere; Discovery Of The Greenhouse Effect It was during the 19th century that scientists realized that gases—such as CO2—found within the atmosphere cause a "greenhouse effect" that regulates the atmosphere's temperature Ironically, the discovery of the greenhouse effect did not happen because scientists were trying to understand global warming




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students
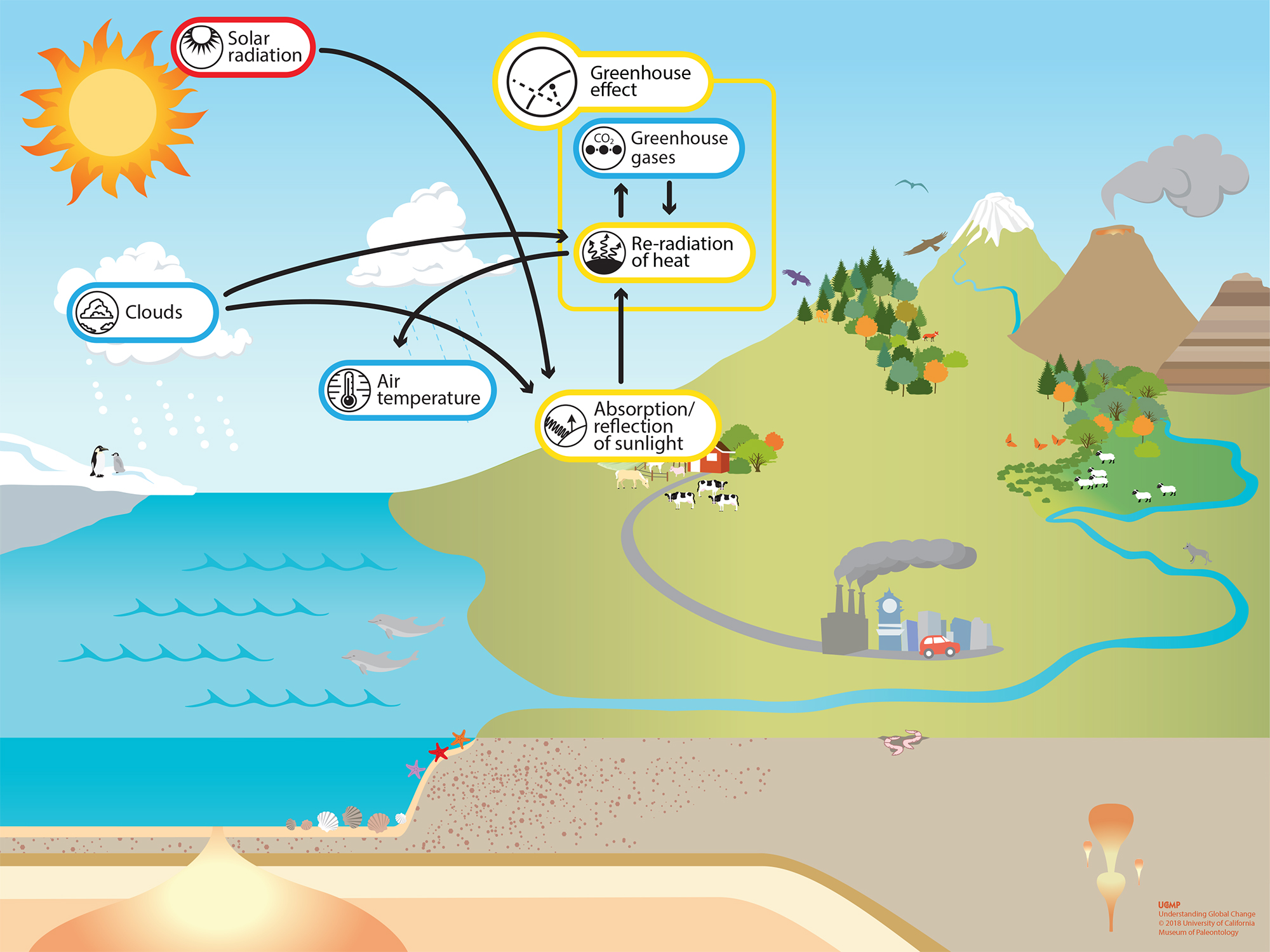



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change
Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) Atmospheric gases like carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide (N 2 O), water vapour, and chlorofluorocarbons are capable of trapping the outgoing infrared radiation from the earth's surface thereby causing greenhouse effect Hence these gases are known as greenhouse gases and the heating effect is known as greenhouseThe greenhouse effect Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere , the Earth would be about 18°C colder on average than it is now That would make it too cold to support life as we know it Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect and climate change Effects of climatic change Resources The greenhouse effect is the retention by Earth ' s atmosphere in the form of heat some of the energy that arrives from the sun as light Certain gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4), are transparent to most of the wavelengths




What Are Greenhouse Gases David Suzuki Foundation



Untitled Document
The greenhouse effect Heat energy provided from solar radiation (light source of the Sun) is the reason why Earth can sustain life presently When this energy hits the surface of the Earth, it reflects back into the atmosphere at a different wavelength, so this outgoing energy becomes infrared radiation In the air, greenhouse gases such asThe Greenhouse Experiment Materials (For a class of 32) 8 sets of crayons or markers (1 per group) Tape for displaying created towns Scissors Butcher paper or end roll of newspaper Time Required 4560 minute period Standards Met S2, S3, S4, S7, G4, G5, L, LA5, LA12 Procedure Draw 8 very simple ecosystems with a mountainous area, small stream and larger river on roll of The greenhouse effect occurs when Earth's atmosphere traps solar radiation because of the presence of certain gases, which causes temperatures to rise
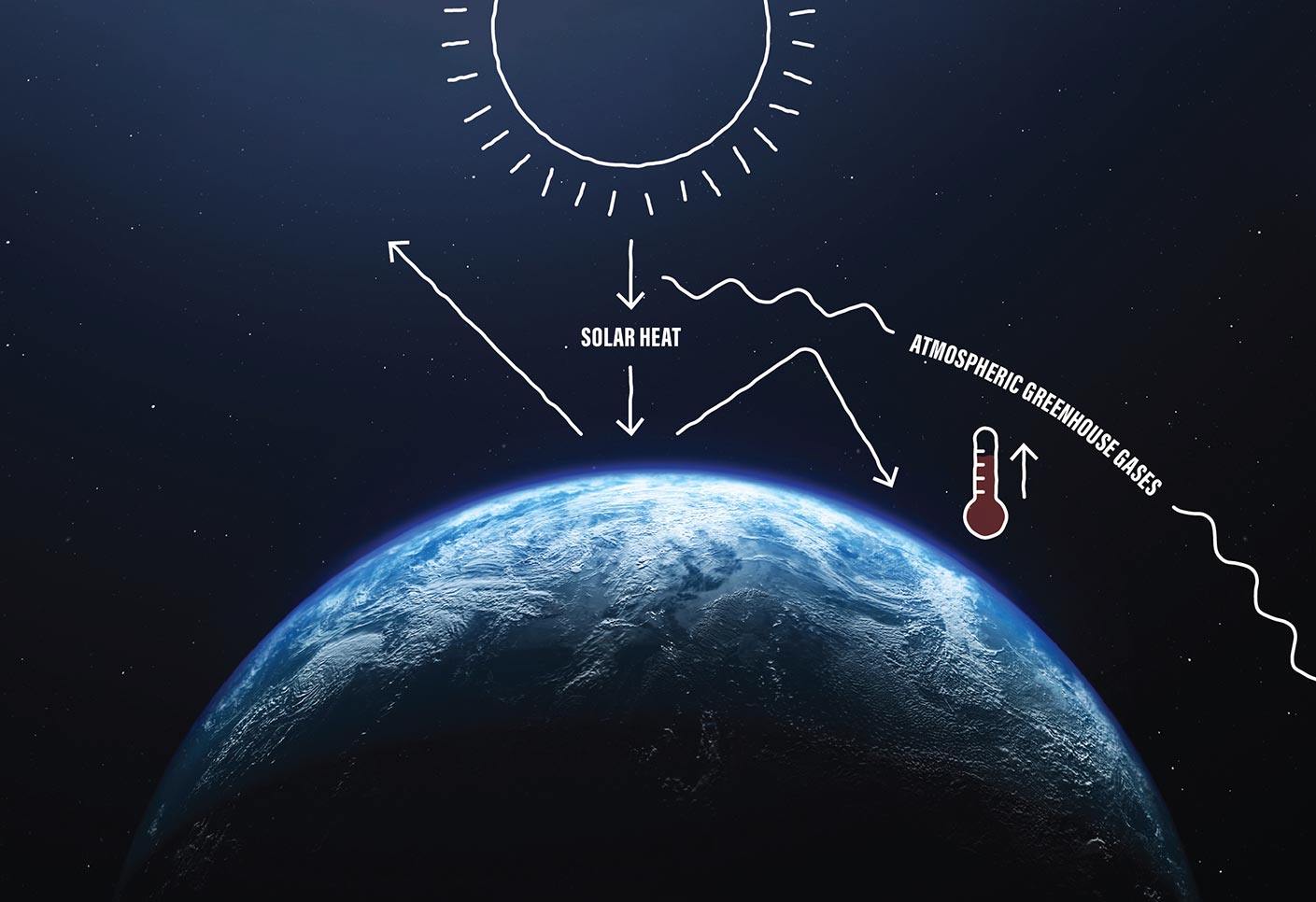



Nasa At Your Table Where Food Meets Methane And The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
With increasing levels of greenhouse gases causing our climate to change, it is important to understand exactly where these gases come from and how they disperse in the atmosphere A new dataset, produced by the European Space Agency's Climate Change Initiative, provides a detailed view of carbon dioxide and methane – two of the most important humanThe greenhouse effect is a good thing It warms the planet to its comfortable average of 59 degrees FahrenheitThe Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (AGGI) is calculated as the ratio of total direct radiative forcing due to these gases in a given year to its total in 1990 1990 was chosen because it is the baseline year for the Kyoto Protocol and the publication year of the first IPCC Scientific Assessment of Climate Change




Greenhouse Effect What Is It Definition And Role In Global Warming




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
Global Warming Global warming is by far the greatest disadvantage of the greenhouse effect A rise in the level of the greenhouse temperature directly contributes to the rising temperature of the planet As the greenhouse gases tend to increase, their ability to trap the heat and radiate it back to the earth's surface also increasesSince the Industrial Revolution in the late 1700s and early 1800s, people have been releasing large quantities of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere That amount has skyrocketed in the past century Greenhouse gas emissions increased 70 percent between 1970 and 04 Emissions of carbon dioxide, the most important greenhouse gas, rose by about 80 percent during that time• The greenhouse effect refers to the physical process by which atmospheric gases allow sunlight to pass through, but also absorb infrared radiation from Earth's surface Thus the atmosphere acts like a heattrapping blanket Life as we know it could not exist on Earth without the warming produced by the greenhouse effect



Greenhouse Gases




What S The Deal With Greenhouse Gases Emissions And The Environment Futurelearn
Greenhouse Gases such as carbon dioxide is the primary cause for the Greenhouse Effect The major contributors to the greenhouses gases are factories, automobiles, deforestation , etc The increased number of factories and automobiles increases the amount ofThe corresponding greenhouse effect is 245 C The adiabatic model allows one to estimate the effect of socalled ''greenhouse gases'' on the temperature regimes of the Earth troposphere and its greenhouse effect For asymptotic estimates, the writers assumed that the nitrogen–oxygen Earth's atmosphere is completely replaced by




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




File Greenhouse Gas By Sector Png Wikimedia Commons




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica




Greenhouse Gases Mit Climate Portal
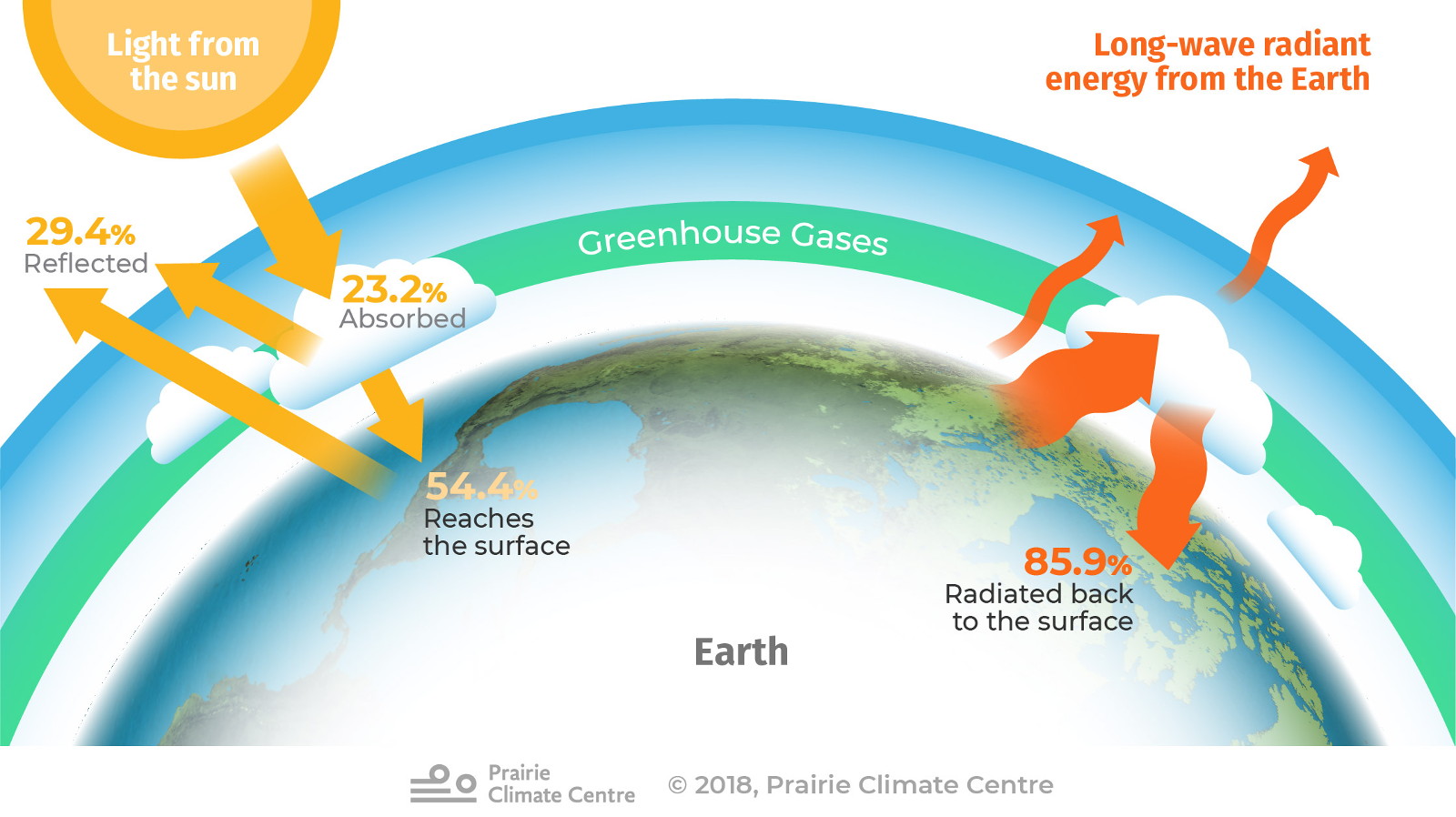



Greenhouse Gases Climate Atlas Of Canada
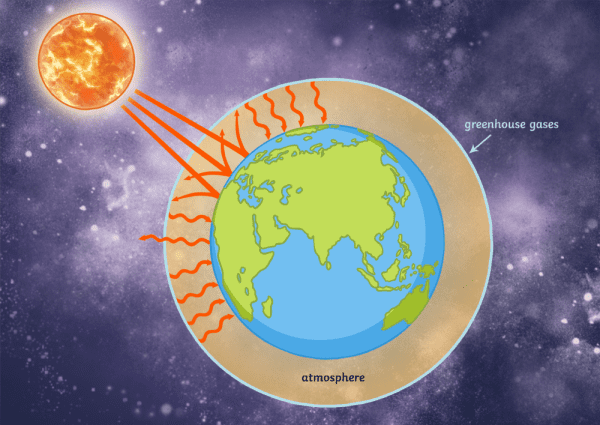



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki



3




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



7 H The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Illustrated




Greenhouse Effect Stock Illustrations 3 348 Greenhouse Effect Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
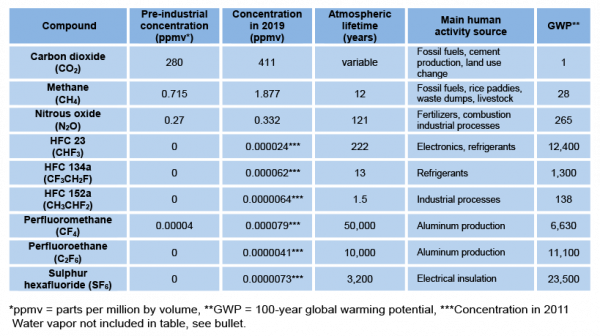



Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
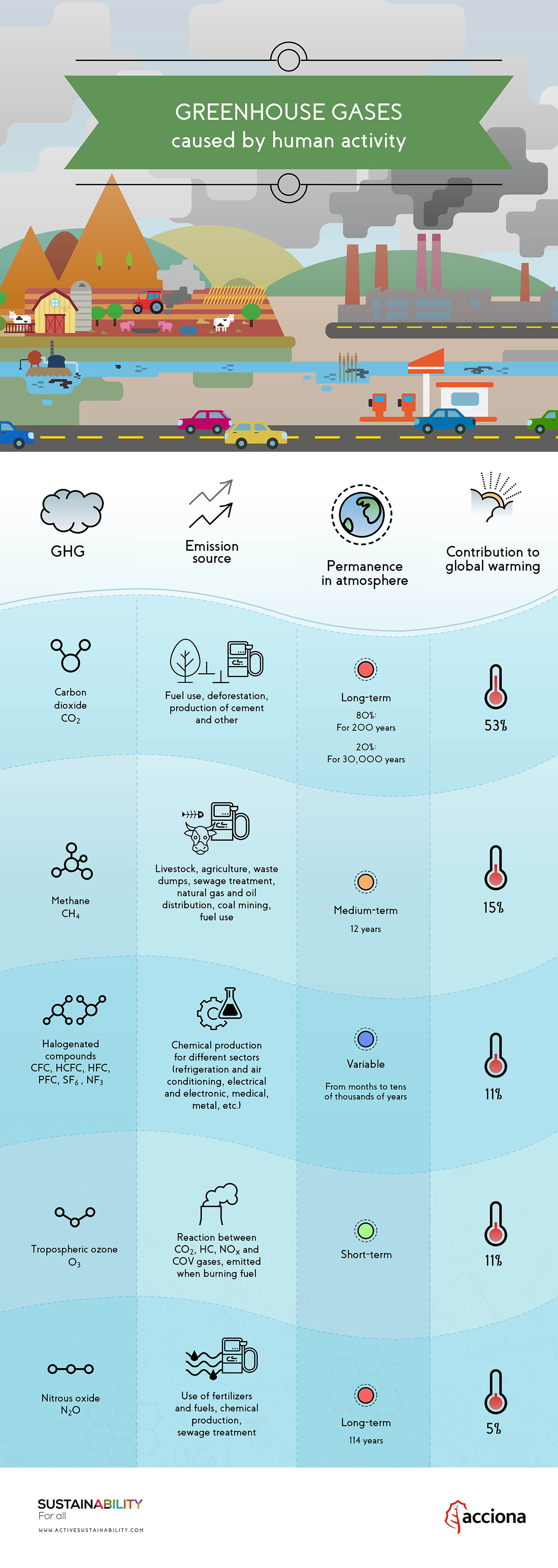



How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Causes And Examples Market Business News



The Greenhouse Effect




Climate Change Greenhouse Gases Britannica




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect Artis Energy




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
.png)



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education



Greenhouse Gases




How Trump Is Ensuring That Greenhouse Gas Emissions Will Rise The New York Times




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Main Sources Infographic What S Your Impact




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
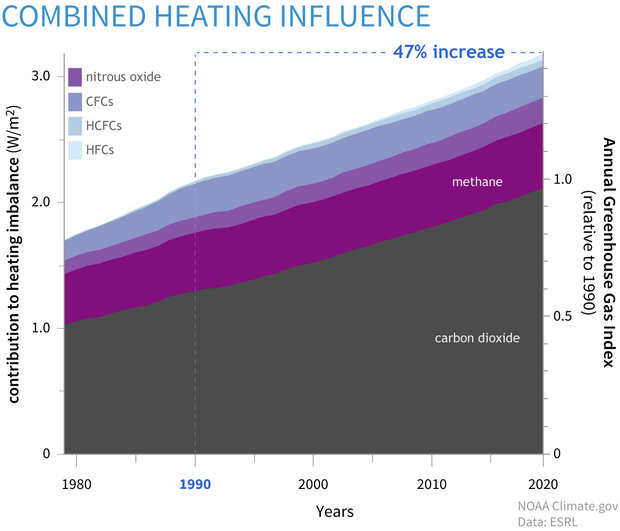



Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization
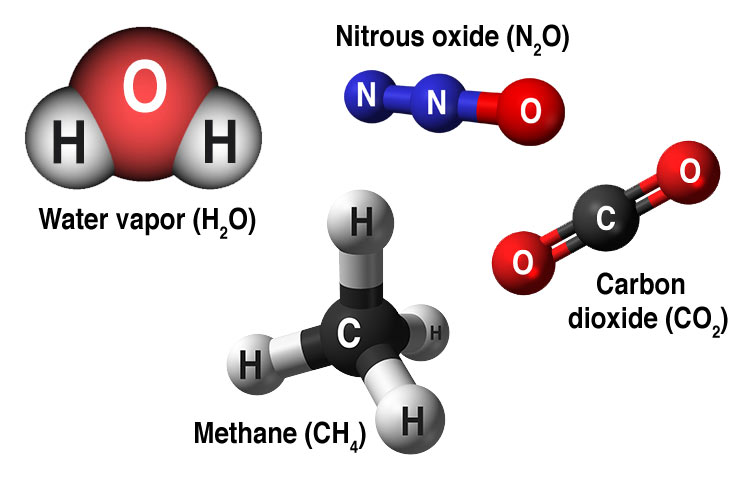



Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
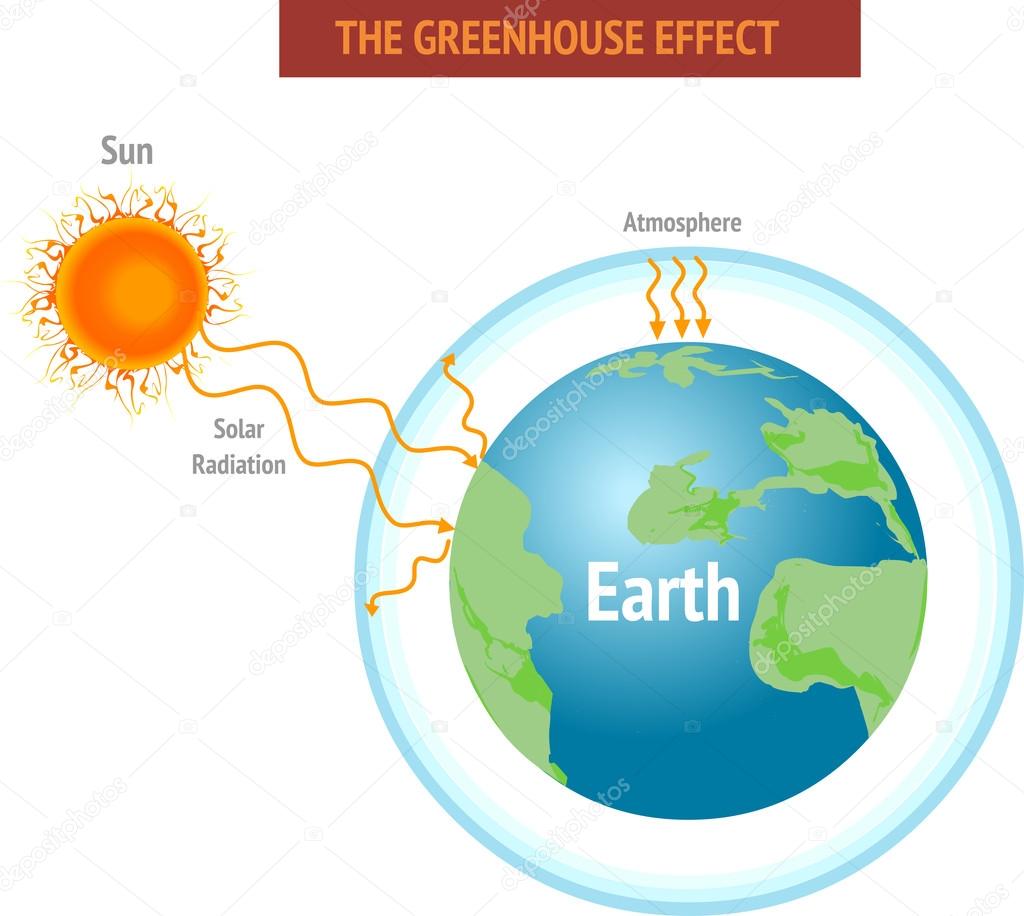



Greenhouse Effect Royalty Free Greenhouse Effect Vector Images Drawings Depositphotos
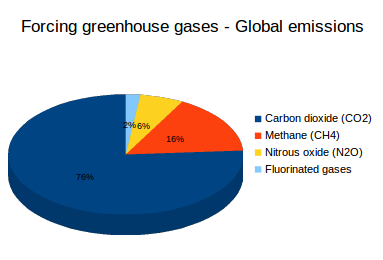



What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact
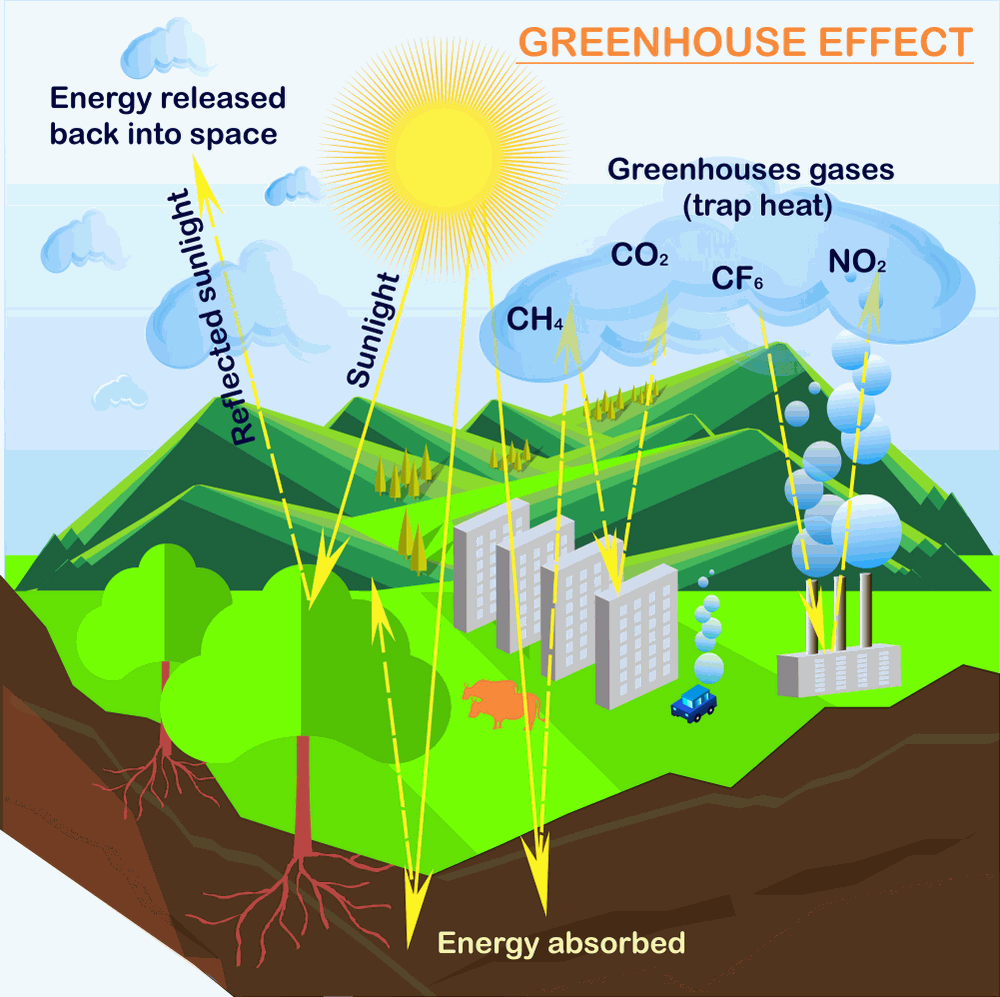



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Global Warming 19




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



Climate Change




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gas Levels Hit A New Record Cuts Fall Short U N Finds




21 962 Greenhouse Gas Photos And Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images




The Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gasses
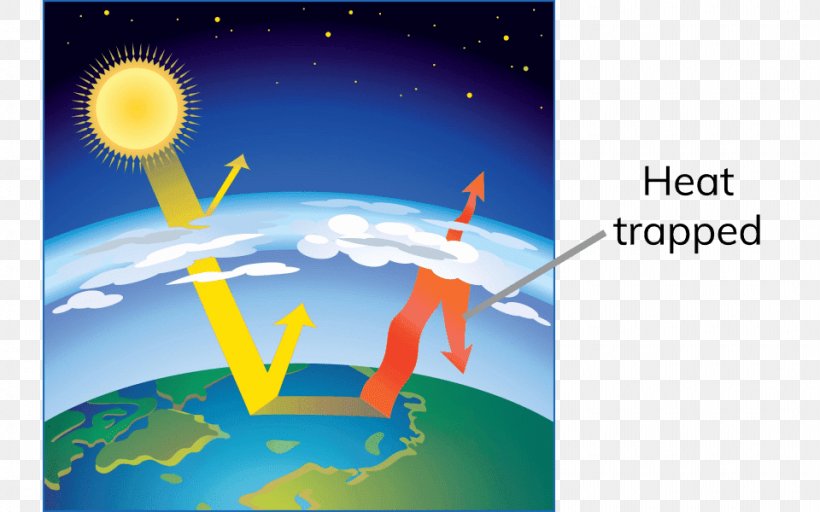



Earth Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Atmosphere Png 960x600px Earth Atmosphere Atmosphere Of Earth Brand Climate Download
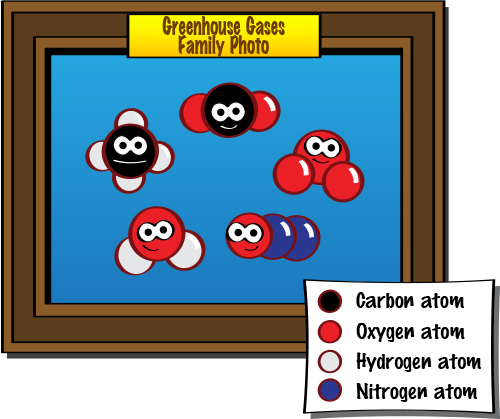



Greenhouse Effect Keeping The Balance Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Again Break Records c News




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



The Greenhouse Effect




What Are The Main Man Made Greenhouse Gases Environment The Guardian




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Youtube




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Effects Of Increased Greenhouse Gas Emissions What S Your Impact




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate



Carbon Dioxide




Greenhouse Gas Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
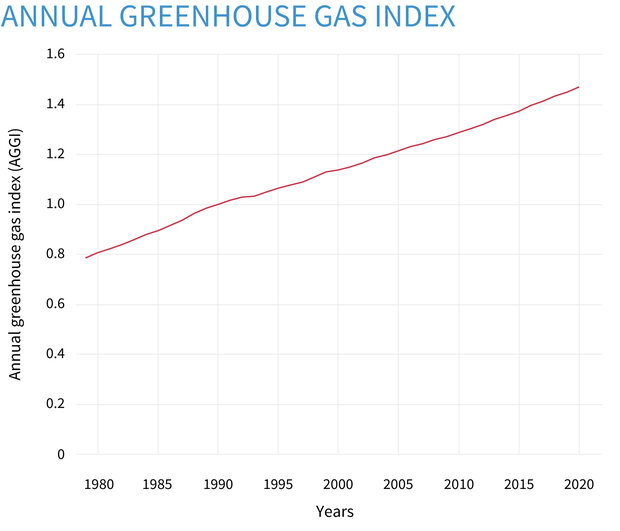



Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
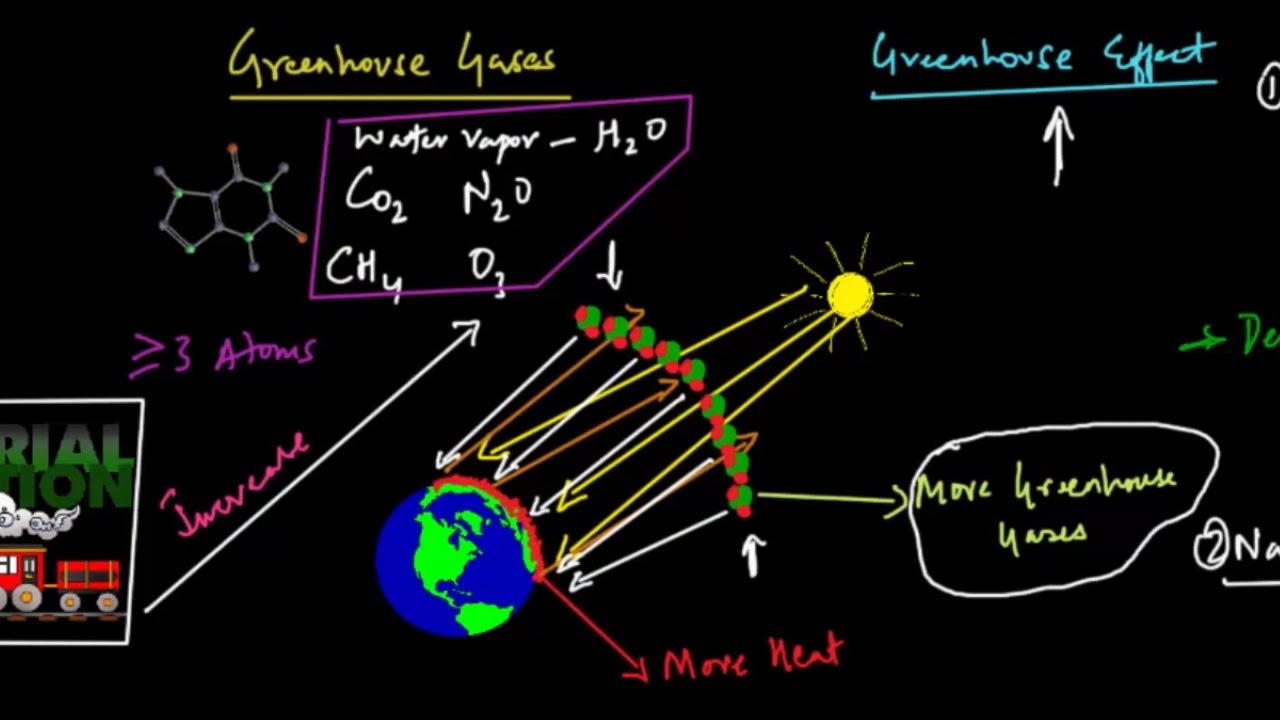



Understanding Greenhouse Gases And Greenhouse Effect Youtube
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/greenhouse-effect-vector-diagram-889624280-6670a804e4d2472eb71892d746c8d0df.jpg)



What Are Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know
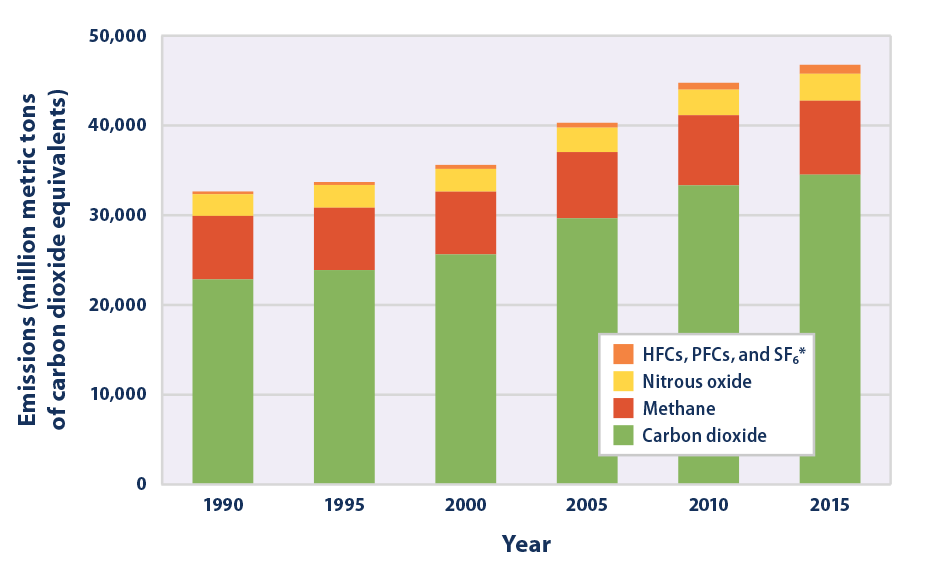



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




The Greenhouse Effect World101



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿